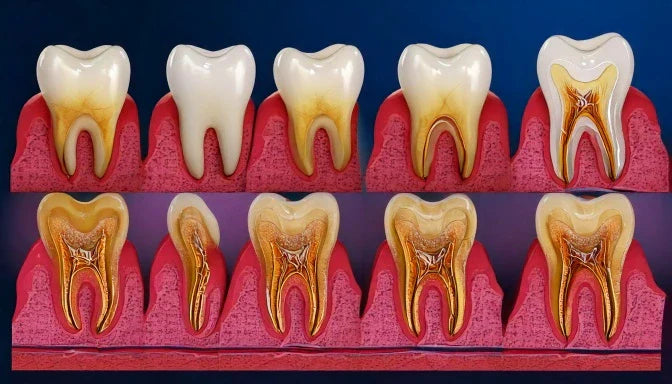
Dental cavities, commonly known as tooth decay, are a widespread oral health issue affecting people of all ages. Cavities—those tiny holes or damage in your teeth—might seem minor initially, but they can lead to serious oral health issues if ignored. From the slight discolouration of enamel to a full-blown toothache, the journey of tooth decay is gradual but preventable.
Understanding how cavities are caused and the available treatments at different stages is crucial for maintaining good oral hygiene and preventing several dental problems. Usually, cavities are caused by poor oral hygiene, consuming sugary foods and bacteria buildup. Recognising the stages of cavity development and acting promptly can save both your teeth and wallet. This article explores 5 stages of tooth decay, treatments at each phase, and practical tips for prevention.
The 5 Stages of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay doesn’t happen overnight. Tooth decay doesn’t start with pain but with subtle signs that are easy to miss. It progresses through distinct stages, each requiring specific care. Tooth decay evolves gradually; understanding the dental cavity stages helps you intervene before the problem worsens. Here we’ll walk through the stages of the cavity, each with its unique characteristics.
Dental Cavity Stages—Details of Each Stage
In the cavity starting stage, the enamel—the hard, outer layer of the tooth—starts to lose minerals. The initial phase is marked by white spots appearing on the teeth; it is actually the cavity-starting stage, which is often ignored. This is where the beginning stages of tooth decay start to manifest.
Stage 1: Demineralization
This is the earliest phase of decay, where the enamel, the tooth’s outermost layer, begins losing minerals due to acid produced by plaque bacteria. At this point, your tooth is still intact; this phase doesn’t involve visible cavities; it’s the cavity starting stage or first warning stage; it is actually the beginning stage of tooth decay. At this stage, you might not feel discomfort, but a close look can reveal white or chalky spots on your teeth. Early cavity treatment can reverse the damage through the tooth remineralisation technique. This stage is reversible with fluoride treatments and a diet rich in calcium and phosphate.
Stage 2: Enamel Decay
If the demineralization isn’t addressed, the enamel starts to break down, forming tiny holes. This is where most people start noticing discomfort or even visible cavities. At this stage, professional intervention is necessary to prevent further damage. This is often categorised as one of the significant dental cavity stages, where fillings are required to restore the tooth. This stage is typically painless, but ignoring it can lead to more severe complications.
Stage 3: Dentin Decay
In the beginning stages of tooth decay, the bacteria penetrate the dentin, the layer beneath the enamel. Once decay reaches the dentin, you’ll likely feel it. Sensitivity to sweets or hot and cold drinks becomes more pronounced. Early cavity treatment can still save your tooth, but delaying treatment will lead to deeper damage.
Stage 4: Pulp Damage
Here’s where things get serious. The decay has invaded the pulp, the innermost layer, which contains nerves and blood vessels. It causes immense pain and inflammation. By this point, the decay has reached one of the most advanced stages of cavity progression. Ignoring it can lead to an infection that can not just affect your oral health but also your overall health. Pain at this stage is intense and persistent. Consulting a dentist immediately is vital to avoid further complications.
Stage 5: Abscess Formation
The final and most severe stage is abscess formation. This painful infection around the tooth’s root can lead to swelling, fever, and even jawbone damage. Immediate dental care is essential at this point, often requiring antibiotics and root canal therapy or extraction. Abscesses are not just dental issues; they can affect your overall health. Prompt treatment is non-negotiable. Recognizing the 5 dental cavity stages and early cavity treatment can help prevent reaching this painful point.

Tips for Preventing Cavities and Maintaining Oral Health
- Early Cavity Treatment: Caught in the cavities' first stage, tooth decay is relatively easy to manage. Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste and using a fluoride rinse are key in reversing the first stage or early damage of teeth. Early detection in the tooth decay stages ensures simpler treatments.
- Stage 2 Cavity Treatment: In tooth decay stages involving enamel decay, dental fillings are the most common solution. The decayed portion is removed, and the cavity is filled with durable material. These treatments prevent further progression to advanced dental cavity stages.
Dental fillings are effective, quick, and relatively less painful. Fillings are made of composite resin, amalgam, or porcelain to protect the tooth from further harm. It’s a quick procedure that can save you a lot of trouble down the line.
Advanced Treatments
- Dentin Decay: At this stage, larger cavities require larger fillings or dental crowns. This phase of the cavity starting stage demands immediate attention to prevent pulp involvement.
- Pulp Damage: At this stage of the cavity, root canal therapy becomes the best option. This procedure cleans out the infected pulp, seals the tooth, and often involves placing a crown for added protection.
- Abscess Formation: An abscess demands immediate attention. Antibiotics will combat the infection, but the tooth may need extraction or an extensive root canal to heal completely. This is the most severe phase of stages of cavity development.
Advanced treatments can be more invasive and costly. To avoid this situation, prevention should be taken at the beginning stages of tooth decay.
Tips for Preventing Cavities and Maintaining Oral Health
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to cavities. Here are some practical tips to keep your teeth healthy.
- Brush and floss daily with a fluoride-based toothpaste. This strengthens the enamel and keeps bacteria at bay.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles that contribute to the beginning stages of tooth decay. Try Perfora’s water flossers for a complete flossing experience.
- Limit sugary and acidic foods that erode enamel, a key factor in the early stages of cavity formation.
- Stay hydrated to maintain saliva production, which neutralizes acid and helps fight bacteria.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. Regular monitoring helps detect and address issues during the cavity's first stage.
Get more cavity prevention tips here.

Conclusion
Cavities are a silent but serious threat to your oral threat. Recognizing the stages of cavity progression early and seeking timely treatment make all the difference. From the cavity starting stage to advanced pulp damage, every phase has a solution if caught in time. By adopting good oral hygiene habits and visiting your dentist regularly, you can keep cavities at bay and enjoy a healthy and radiant smile.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the stages of a cavity?
Answer- The stages of the cavity consist of Dimineralization, Enamel Decay, Dentin Decay, Pulp Damage, Abscess Formation.
2. What is Stage 2 cavity treatment?
Answer- Stage 2 of the cavity treatment involves filling the cavity in the enamel, which prevents further progression and restores the tooth’s structure.
3. What is the process of treating a cavity?
Answer- Early stages involve fluoride treatments and sealants, while advanced stages may require fillings, root canals, or extractions based on sensitivity.